The Science
Tribbles 2 inhibition
Tribbles 2 (Trib2) is a protein that acts as a scaffold for a wide range of enzyme functions important to a cell’s function and survival.
This general support role means that Trib2 has wide powers, and that means that when Trib2 misbehaves, it can be responsible for a wide range of diseases. Despite being identified as a priority drug target in cancer and autoimmune diseases, the task has proved elusive with no anti-Trib2 drug developed to date.
Finding an anti-Trib2 drug remains a top priority in medicine.
The need to find a Trib2 inhibitor has been become even more urgent with recent findings that when it comes to cancer, excessive Trib2 activity:
- promotes tumour aggression (Trib2 is linked to aggressive forms of melanoma, lung, liver, brain and colorectal cancers, neuroendocrine tumours (NETS) and acute myelogenous leukemia)
- blocks protective immune responses, allowing cancer cells to flourish
- promotes resistance to chemotherapy, resulting in treatment failure
- promotes inflammation, helping to create a tumour environment that encourages cancer growth.
In an important breakthrough, Filamon has achieved this goal with the first known anti-Trib2 drug that:
- Blocks Trib2 function specifically by causing its degradation.
- Importantly has shown itself to be very well tolerated in humans.
- Gives Filamon a clear lead in the field, with doctors, patients and the pharmaceutical industry keenly watching the outcome of clinical trials.
FLM-JG1 An important new multi-functional drug candidate
FLM-JG1 is the re-purposed anti-viral drug, daclatasvir. Developed by Bristol Myers Squibb as a treatment for Hepatitis C infection, daclatasvir was withdrawn from global markets in 2018 when superseded by a more effective anti-viral drug.
Daclatasvir was identified serendipitously by US researchers in 2020 (led by Filamon’s major shareholder, Henry Ford Health (HFH), a premier academic medical centre based in Detroit, Michigan, USA), as a potent inhibitor of Trib2 in an action unconnected to its anti-viral action, with the U.S. researchers obtaining allowance from the US and EC patent offices for claims as an anti-cancer agent. Filamon has an exclusive global license to this valuable IP.
hGIIA-sPLA2 inhibition
The enzyme, Group IIA secretory phospholipase A2 (hGIIA-sPLA2) is a major regulator of the inflammatory response – a ‘bottleneck’ in every cell’s outer membrane through which inflammatory signals need to pass and be directed to the appropriate action.
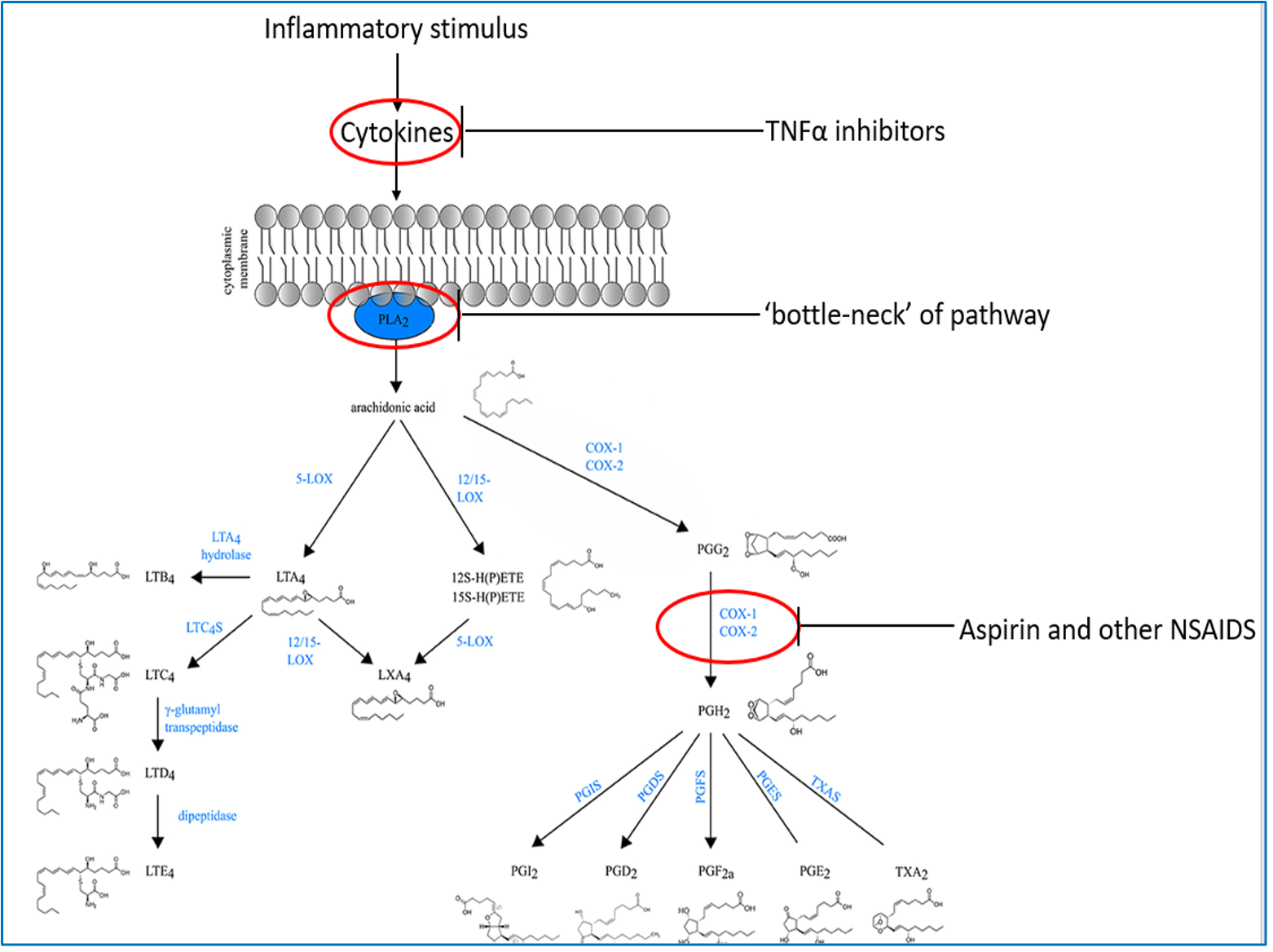
This key regulatory role makes any error in hGIIA-sPLA2 behaviour a major risk factor in cardiovascular disease (atherosclerosis), acute inflammation (asthma), hyperacute inflammation (cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19 and CAR-T cancer therapy), chronic inflammatory/ autoimmune diseases and cancer.
In cancer in particular, the inflammation stemming from abnormal hGIIA-sPLA2 function results in the promotion of tumour growth, angiogenesis (new blood vessel growth), invasiveness and immune evasion.
Given this enzyme’s ‘master switch’ role in inflammation, a drug able to block hGIIA-sPLA2 would be a highly valuable multi-functional medicine.
Existing anti-inflammatory drugs either work above hGIIA-sPLA2 (eg, Humira, Remicade) or below it (eg, Ibuprofen), but none target this bottleneck itself.
Major efforts by industry to develop an inhibitor of hGIIA-sPLA2 have failed because of toxicity, reflecting this enzyme’s critical role in health.
Filamon is confident it has solved the toxicity problem with its drug, FLM-c2
FLM-c2. An important new multi-functional drug candidate.
FLM-c2 selectively targets the enzyme’s abnormal roles in disease while sparing its critically important normal roles in maintaining health.
FLM-c2 represents a 2-step, major breakthrough in hGIIA-sPLA2 inhibition:
- FLM-c2 specifically inhibits the non-catalytic (enzymatic) functions of hGIIA, sparing its essential catalytic functions that maintain health.
- FLM-c2 works by blocking the binding of hGIIA-sPLA2 to the microfilament – vimentin – a major co-factor in multiple signaling pathways involved in inflammation and cancer.
These 2 steps account for the greater safety of FLM-c2 compared to earlier sPLA2-hGIIA inhibitors.
Filamon believes its hGIIA-sPLA2 inhibiting technology has the potential to revolutionise the treatment of both acute and chronic inflammation across multiple disease states including cancer.
- FLM-c2 is an oral cyclic peptide that has undergone extensive pre-clinical testing, confirming its ability to inhibit human prostate cancer cell growth in mice, as well as safety and tolerability in rodents and dogs.
- FLM-c2 has successfully completed a Phase 1 safety, bioavailability and preliminary efficacy study in prostate cancer patients.
- Patents pending on FLM-c2 as a well-tolerated anti-inflammatory across a range of diseases due to its unique mechanisms of action.
- Aiming to block inflammation in aggressive cancer behaviour, recognising that elevated hGIIA activity is linked to aggressive cancer growth and poor survival outcomes in a wide range of cancers like prostate, breast and lung cancers.
JUN/FosB/DFosB modulation
FLM-BT2 is a uniquely acting drug candidate delivering effective drug actions on key disease malfunctions that other drugs have struggled to do.
At the heart of every cell’s ability to survive and grow and function is a group of proteins with names such as MEK, ERK 1 and 2, JNK, JUN, NFkB, FosB and DFosB. The particular proteins of interest here in this grouping are ERK/JNK/JUN/FosB/DFosB.
Just like Tribbles 2 and hGIIA-sPLA2, ERK/JNK/JUN/FosB/DFosB
- are responsible for many of the fundamental functions that ensure a cell can survive and function normally.
- which means that any malfunction will make humans prone to a range of diseases.
- which in the case of ERK/JNK/JUN/ FosB/DFosB involves diseases as diverse as cancer, autoimmune disease and neurological conditions such as addictive behaviour (eg, drug addiction).
- and which because of their critical importance to human health means that any attempt to block their action carries a high risk of serious side-effects.
FLM-BT2 offers an entirely new approach by correcting an unbalanced interaction between the different proteins (ERK/JNK/JUN/ FosB/DFosB) rather than singling out individual proteins and risking upsetting the balance further.
|
In the case of abnormal blood vessel growth in cancer generally and in the eye in macular degeneration…
|
|
FLM-BT2 suppresses ERK/c-JUN/FosB/ΔFosB expression
|
Blocks their formation and leakiness, while normal blood vessels remain unaffected.
|
|
In T-cells (immune cells) in cancer…
|
|
FLM-BT2 increases JNK/c-JUN expression, but leaves ERK expression unaffected.
|
Reduces expression of PD-1 and reverses markers of T-cell exhaustion.
|
|
In cancer cells…
|
|
FLM-BT2 increases c-JUN expression, reduces ERK expression and leaves JNK expression unaffected.
|
Results in cancer cell death
|

